by Comite Web | Dec 16, 2025 | Sin categorizar
This study conducted by researchers from Vigo presents an innovative sequential therapeutic strategy against pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, one of the most lethal cancers due to its stromal barrier that prevents drug penetration.
The novelty lies in the biphasic and sequential treatment: first, lipid nanoparticles containing siRNA that silence the transcription factors YAP1 and FOSL1 are administered, weakening the tumor’s protective stroma; then combination chemotherapy (entinostat and gemcitabine) is applied, which penetrates more effectively into the now permeable tumor tissue.
Results in preclinical models (mouse xenografts and patient organoids) demonstrated reduced fibrotic tissue, increased drug penetration and superior therapeutic efficacy. This approach represents a paradigm shift from traditional combination therapies.
Immacolata Maietta, Patricia Domínguez Arístegui, Iban González Álvarez, Omayra Rodríguez Atanes, Eva María García Fontán, Susana Teijeira Bautista, África González-Fernández, Rosana Simón-Vázquez, Sequential YAP1/FOSL1 silencing and epigenetic therapy to overcome stromal barriers in pancreatic cancer, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2025, vol. 684, 126155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.126155.
Access the full article at the following link: https://pdf.sciencedirectassets.com/271189/1-s2.0-S0378517325X00156/1-s2.0-S0378517325009925/main.pdf?X-Amz-Security-Token=IQoJb3JpZ2luX2VjEKX%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FwEaCXVzLWVhc3QtMSJHMEUCIEmy%2FlDACu%2BJwqxPbPi%2B%2FdT8L3F3qWlzvnC2iVZ8xzfLAiEAiQlAXbjBadOgjBg8Wl%2BrHpj2eQpEWLzo4KCl6C6r4eAqswUIbhAFGgwwNTkwMDM1NDY4NjUiDN1865%2B9jlmTrQV6mSqQBaBj4CJJhNs7rR9%2FaKngxlEdVyp3ciVQDZ86XZQRWnw%2FonwJX3RAqszW3YWaaFbzNVdRDwsWyEqwvnldCO3fKo%2BZZmH%2Fw4zIkdGCq2OSY31%2Bv3lpio2zYlE6Rq8su75k1ZreitM81AmUfjbJB%2FCNwFoFaREMHgtGqWJKCx0%2FeTc8pofkmPmmpbm%2BF%2Bu3JdrtXZ5Zt885mqylBP0zXDovPhguqx%2BpQT8hzMhSRU20mx7Z5P6UM0VpCKx%2BGYHXqN6%2BbEyiybTi1Q2iFPG7t%2BUjpOZEKZZLdezVm%2BC9O2Q0FVzgsC63ffGKPCLS%2BH2hUdfSxzSWq9ij14MiH2h1jlsjGdw4xUDuL4uXesK5ezbyy6JT6%2FH46QdNZvitErBc5d8cfkNHhL0I%2F0GARzLYyOkjhFlZBCjKiH83gkLH0wEjSo2k5aHOLr4Ts49WrF9k8vL5fXEGO7fSSjPCnaV8DB43SO0l6vPHX%2BydavJF59AvMtuijHUxs6wmgzBulOsphtep2V5NDexVilR9IhpJtHOMR15876hFAF%2By3W7W%2FhjuHsnRaTQ3Rw7VHMQB%2BNGzd9JdZ5BQKjh%

by Comite Web | Dec 15, 2025 | Sin categorizar
by Comite Web | Dec 10, 2025 | Sin categorizar
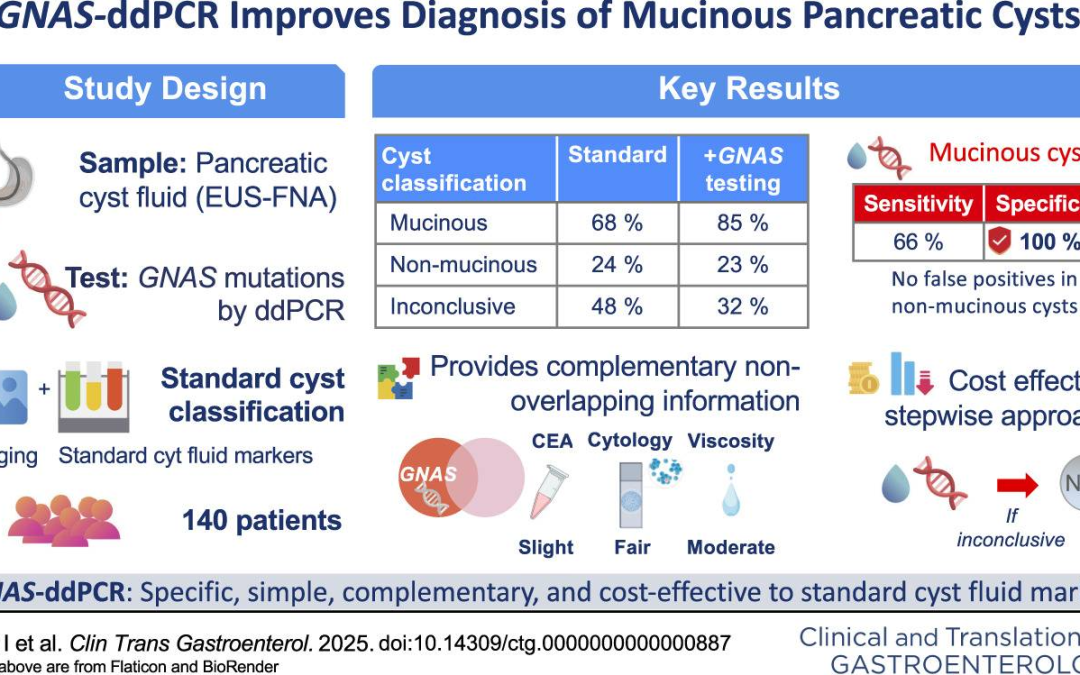
The analysis of GNAS mutations using ddPCR in fluid obtained through endoscopic ultrasound–guided fine-needle aspiration has proven to be a useful and cost-effective diagnostic tool for evaluating mucinous pancreatic cystic neoplasms.
This technique can be applied before turning to more expensive multigene sequencing panels, which can be reserved for cases in which no GNAS mutations are detected and alternative non-mucinous etiologies need to be explored.
Overall, this strategy represents a practical advance that improves diagnostic accuracy and optimizes resource use in the assessment of pancreatic cystic neoplasms.
Araujo IK, Soy G, Ginès A, Sendino O, Fernández-Esparrach G, Sánchez-Montes C, Cuatrecasas M, Archilla I, Montironi C, Silvia A, Ausania F, Domínguez-Fraile M, Villagrasa V, López-Guerra M, Colomer D, Vaquero EC. Single GNAS Droplet-Based Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of Pancreatic Cyst Fluid: An Effective Up-Front Strategy for Mucinous Cyst Diagnosis by Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025 Sep 1;16(9):e00887.
Link to PDF: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12456567/pdf/ct9-16-e00887.pdf
Link to the group web: https://alipanc.org/grupo/pancreas-idibaps-clinic/

by Comite Web | Dec 10, 2025 | Sin categorizar
A study led by the Experimental Oncology Group at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) has described a triple-combination therapy for pancreatic cancer. The work has been published in the prestigious journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
The study shows that genetic ablation of three key nodes in KRAS signaling (RAF1, EGFR, and STAT3) leads to complete and permanent regression of orthotopic PDAC tumors driven by KRAS/TP53 mutations. Similarly, a drug combination targeting KRAS (RMC-6236/daraxonrasib), EGFR (afatinib), and STAT3 (SD36) induces full tumor regression with no resistance observed for over 200 days. This triple therapy proved effective in both genetically engineered mouse models and patient-derived xenografts, without tumor relapse. Importantly, the treatment was well tolerated. Although the findings support the development of clinical trials based on this combined strategy to improve PDAC therapy, alternatives to afatinib and SD36 will be needed to facilitate clinical translation by reducing toxicity and improving ADME properties, respectively.
This finding opens the door to exploring these therapeutic avenues and guiding the development of new clinical trials that could benefit patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Link to ➡️ Full article
Links to Research group ➡️ Experimental Oncology ALIPANC, Experimental Oncology CNIO.
by Comite Web | Dec 9, 2025 | Sin categorizar
On December 2, 2025, ALIPANC held its Extraordinary General Assembly to ratify the results of the electoral process for the Management Committee. The online voting system ensured transparency and participation, reaching 58% of elegible voting groups.
Management Committee 2025-2026
The 13 elected members are:
Francisco X. Real, Teresa Macarulla, Justo Castaño, Jorge Adeva, Alfredo Carrato, Silve Vicent Cambra, Elisa Espinet, Meritxell Rovira, Raquel Benítez, Francisco Barriga, Fabio Ausania, Carmen Guerra and Andrés Muñoz.
This team combines profiles in basic research (61.54%) and clinical research (38.46%), reinforcing a comprehensive approach to pancreatic cancer.
Next steps
In the coming days, positions (President, Vice-President, Secretary, Treasurer and Members) will be assigned, and the strategic plan for 2026 will be defined.

by Comite Web | Dec 9, 2025 | Sin categorizar
On November 21, ALIPANC held its 4th Solidarity Gala Dinner at the Élkar restaurant in Madrid, coinciding with World Pancreatic Cancer Day. The main goal was to raise funds to boost pancreatic cancer research, a disease that remains one of the greatest challenges in oncology.
An event to unite science and solidarity
The gala brought together healthcare professionals, researchers, patients, and partners in a unique gastronomic space with spectacular city views. The evening included a welcome cocktail, an institutional update on research progress, and a solidarity dinner.
During the event, patient experiences were shared, and current challenges in the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer were addressed. The highlight was the charity raffle and auction, featuring exclusive products and artworks donated by companies and artists.
Participation and collaboration
The dinner gathered 46 in-person attendees and 20 virtual participants (Fila 0), demonstrating the commitment of the scientific and social community. All funds raised will be allocated entirely to research projects promoted by ALIPANC.
Among the collaborating companies were Casa Mas, Leroy Merlin, One Shot Hotels, Seaside Hotels, INMOA and Deoleo. The works auctioned were by artists such as Jordi Franquesa, Ken Moser, Pierre Savater and Juan Pita.




