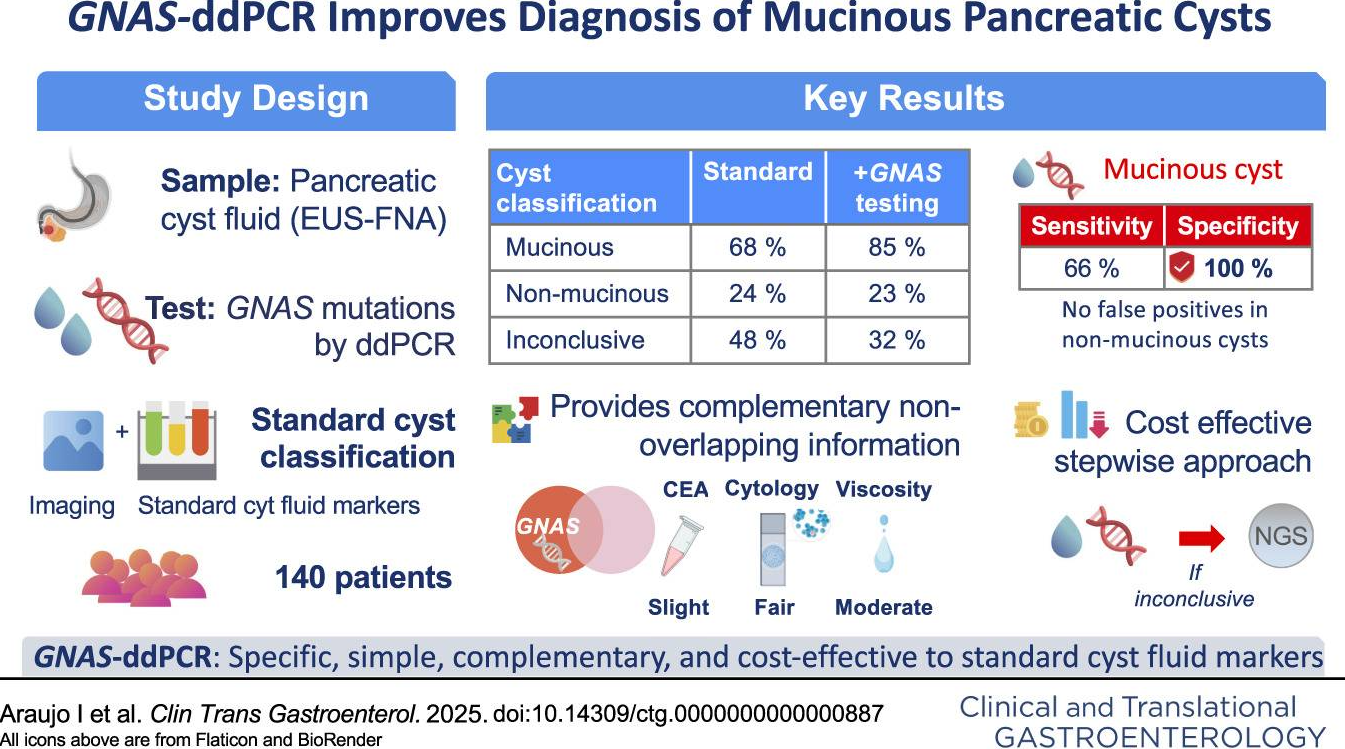
The analysis of GNAS mutations using ddPCR in fluid obtained through endoscopic ultrasound–guided fine-needle aspiration has proven to be a useful and cost-effective diagnostic tool for evaluating mucinous pancreatic cystic neoplasms.
This technique can be applied before turning to more expensive multigene sequencing panels, which can be reserved for cases in which no GNAS mutations are detected and alternative non-mucinous etiologies need to be explored.
Overall, this strategy represents a practical advance that improves diagnostic accuracy and optimizes resource use in the assessment of pancreatic cystic neoplasms.
Single GNAS Droplet-Based Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of Pancreatic Cyst Fluid: An Effective Up-Front Strategy for Mucinous Cyst Diagnosis by Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle AspirationClin Transl Gastroenterol. 2025 Sep 1;16(9):e00887.
Link to PDF: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12456567/pdf/ct9-16-e00887.pdf
Link to the group web: https://alipanc.org/grupo/pancreas-idibaps-clinic/